
前言
最近我朋友問了我一個關於一個小數轉進制的題目,雖然我當時很忙,但最後我還是抽出了時間幫忙解決,解題的一開始我以為題目挺簡單的,但在解題過程發現還蠻多小技巧要使用,我會在這篇文章分享我的解題過程。
題目
我先給各位看一下題目。
Objective
Programming using basic data types and control structures.
Specification
Write a program which converts a base-S floating point number with value in the range [0,1) to its equivalent base-D representation, where S, D =2, … , 10.
You program should be able to convert an input number with at least 8 significant digits而且.
Hint: Use input/output manipulators std::setw, std::setfill, and std::setprecision to format the output.
Sample run
Base conversion for numbers [0,1) with at least 8 significant digits.
Convert a number from base-S to base-D (2<=S<=10, 2<=D<=10):
Input S: 4
Input D: 9
Input a number [0,1)in base-4: 0.12341234
Error: 0.12341234 is an invalid base-4 number
Input a valid base-4 number: 0.12301230
0.12301230(4) is equivalent to 0.42352295(10) & 0.37266541(9)
Process another Conversion or Quit? (C/Q) C
Convert a number from base-S to base-D (2<=S<=10, 2<=D<=10):
Input S: 8
Input D: 5
Input a number in base-8: 0.66666666
0.66666666(8) is equivalent to 0.85714281(10) & 0.41203241(5)
Process another Conversion or Quit? (C/Q) Q
Note:
Ÿ Download the grade sheet as the cover page of your homework report.
Ÿ You may check the base converter for the assessment of your results.題目理解
這題目要我們先輸入我們想要轉換的進制,從 base-S 進制轉成 base-D 進制,接著要輸入一個至少小數點後有 8 位的小數,首先判斷該小數是否是否符合 base-S 的進制,如果不符合就重輸入,符合就轉進制,最後格式化分別輸出 10 進制與 base-D 進制的小數。
程序設計思路
-
在決定小數的類型時,我們需要知道:
- float 類型的有效數字為 6 ~ 7 位
- double 有效數字 15 ~ 16 位
- long double 有效數字 18 ~ 19 位
根據題目要求至少輸入小數點後有 8 位有效數字,我們應該選擇 double 類型為我們的小數類型。
-
在全程使用 double 類型的變數存取小數時,會遇到數字精確度的問題,也就是在取小數位數時或是在轉換時數字的累加上,極有可能碰到數字尾部(有效數字外)出現了不知所然的位數,導致精確度不準確,也順帶影響運算結果。
為了避免這種情況,我們需要使用 String 類型來存取我們輸入的小數,以獲取我們輸入時的小數位數有多少,再利用位數使用循環將字符串轉成 double 類型,這一步我們主要就是小數位數,後面關於進制檢查與轉換都要用到小數位數。
-
在依序獲取小數每位數字時,可以先乘 10,再使用
(int)強制轉換類型取得整數部份,將乘 10 的小數減去整數部份,持續循環。 -
題意不會要我們轉換 10 進制以上的小數(2 <= S <= 10, 2 <= D <= 10),這代表我們不需要擔心遇到英文字母,但遇到了其實也不麻煩,只要在轉換的地方添加字母條件去- 判斷是否為字母。
-
我們需要優先將小數轉成 10 進制,再轉成其他進制,這樣會有效讓我們去設計算法,如果是設計一個函式通用所有的轉制會很吃力。
-
從非 10 進制轉換到 10 進制的演算法,我們使用指數加權法:

e.g.

代碼實現
int n = -1; // the power of n double base10 = 0; // copy convert1
// Continuously taking decimal places // convert to base-10 for(int i = 0; i < significant; i++) { number *= 10; *convert1 += (int)number * pow(S, n); // e.g. 1.1 (base-2) -> 1*2^0 + 1*2^(-1) = 1.5 (base-10) number -= (int)number; n -= 1; }-
從 10 進制轉成非 10 進制的演算法,我們使用餘數乘積法:
註:來源參考 - 十进制小数转二进制小数方法

e.g.

代碼實現
base10 = *convert1; // copy n = -1; // init // Continuously taking decimal places // convert base-10 to base-D /* Because the precision of double is 16 , so multiply it by 17 and execute at least 17 times, otherwise it will enter an infinite loop. */ for(int i = 0; i < 17; i++) { base10 *= D;
*convert2 += (int)base10 * pow(10, n); base10 -= (int)base10; n -= 1;
if(base10 == 0) // End early { break; } }- 在輸出時使用 API 提供的函式格式化。
cout << setiosflags(ios::fixed) << setprecision(8);- 使用 GDB 進行調試,這樣能快速找到代碼問題。
Functions
- int main() :主程序
- double Scan(string, int *):輸入 string 的小數,轉換成 double 類型,並計算輸入小數的小數位數
- bool isValid(double, int, int):判斷輸入的小數是否符合 base-S 進制
- void convert(double, int, int, double *, double *, int):先將小數轉成 10 進制,再轉成 base-D 進制
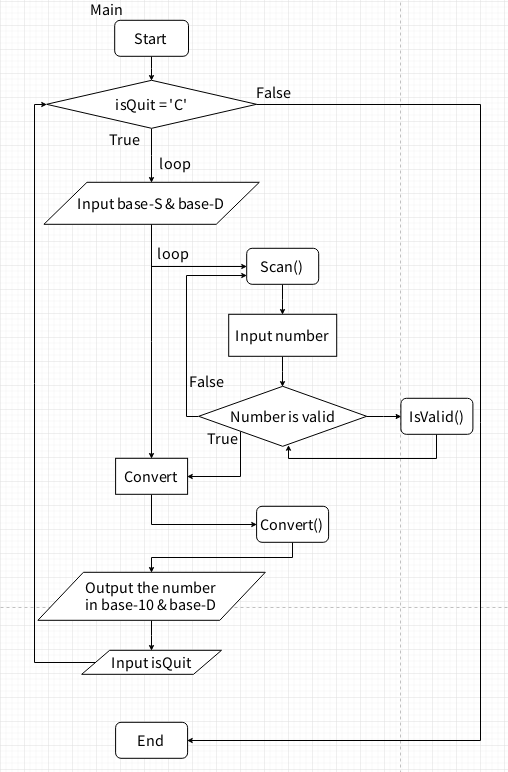
流程圖
此圖為我設計的流程圖。
註:不知道為什麼我從 draw.io 導出的圖片在 linux 下會跑版,格式亂了╮(╯_╰)╭ 最後只好使用截圖工具
源代碼
這裡還是強調一下,寫代碼時註解真的很重要,你的代碼不僅是要你自己可以快速釐清自己的代碼,不然一段時間後自己再看自己寫的內容又看不懂,而且要讓看你代碼的人能看懂。
#include<iostream>#include<math.h>#include<iomanip>#include<string>#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
double Scan(string, int*); // count significantbool isValid(double, int, int); // Judge the number's correctness (Base-S)void convert(double, int, int, double *, double *, int); // convert the number from Base-S to Base-D and Base-10
int main(){ // initialize double number = 0; // The number we need to input int S = 0; // base-S int D = 0; // base-D char isQuit = 'C'; // Judge whether to leave double convert1 = 0, convert2 = 0; // the result from convert() string count; // The number we need to input int significant = 0; // the number's significant
// loop, if isQuit's value is 'Q',break it. while(isQuit == 'C') { // description cout << "Base conversion for numbers [0,1) with at least 8 significant digits.\n"; cout << "Convert a number from base-S to base-D (2<=S<=10, 2<=D<=10):\n"; // input Base-S cout << "Input S: "; cin >> S; // input Base-D cout << "Input D: "; cin >> D; fflush(stdin);
// loop while(1) { // input number cout << "Input a valid base-" << S << " number: "; // cin >> number; number = Scan(count, &significant); if(isValid(number, S, significant)) // number is valid { break; } else // number is invalid { cout << "Error: " << setiosflags(ios::fixed) << setprecision(8) << number << " is an invalid base-" << S << " number\n"; } }
convert(number, S, D, &convert1, &convert2, significant); // convert
// output the result cout << setiosflags(ios::fixed) << setprecision(8) << number << "(" << S <<") is equivalent to " << convert1 <<"(10) & "<< convert2 <<"("<< D << ")"<<endl;
// input isQuit cout << "Process another Conversion or Quit? (C/Q) -> "; cin >> isQuit; // Letters into uppercase isQuit = toupper(isQuit);
// initialize the values convert1 = 0; convert2 = 0; significant = 0; } system("pause"); return 0;}
double Scan(string count, int *significant){ *significant = 0; double number = 0; // we need to enter int N = -1;
cin >> count; // enter the string fflush(stdin);
for(int i = 2; i < count.length(); i++) // use count's length to loop { *significant += 1; // count significant
number += (count[i] - '0') * pow(10, N); // char -> double N -=1; } return number;}
bool isValid(double number, int S, int significant){ double swapDouble = 0;
// Continuously taking decimal places for(int i = 0; i < significant; i++) { number *= 10; if((int)number >= S) // not meets Base-S { return false; // invalid } else { swapDouble = (double)((int)number); number -= swapDouble; } } return true; // valid}
void convert(double number, int S, int D, double *convert1, double *convert2, int significant){ int n = -1; // the power of n double base10 = 0; // copy convert1
// Continuously taking decimal places // convert to base-10 /* Reference https://notfalse.net/17/positional-numeral-systems-conversion */ for(int i = 0; i < significant; i++) { number *= 10; *convert1 += (int)number * pow(S, n); // e.g. 1.1 (base-2) -> 1*2^0 + 1*2^(-1) = 1.5 (base-10) number -= (int)number; n -= 1; } base10 = *convert1; // copy n = -1; // init // Continuously taking decimal places // convert base-10 to base-D /* Because the precision of double is 16 , so multiply it by 17 and execute at least 17 times, otherwise it will enter an infinite loop.
Reference https://www.cnblogs.com/upzone/articles/1389365.html
*/ for(int i = 0; i < 17; i++) { base10 *= D;
*convert2 += (int)base10 * pow(10, n); base10 -= (int)base10; n -= 1;
if(base10 == 0) // End early { break; } }}運行結果

結論
測試輸入測資,輸出與測資結果相同。
相信這題能幫助許多人能對小數進制轉換這類題目有所了解,並增進程序設計中的核心 — 演算法。祝各位學習順利,我也建議各位多主動做題目,積極去學習,這樣才會有所成長。
